
Deploy Dataverse Tables with Macro Templates Easily
Unleash Power Platform Efficiency: Dataverse Tables with Custom Macro Templates
Key insights
- Combining Dataverse Tables and VBA Macros offers a unique solution for deploying complex document templates within Power Platform projects, especially useful in environments with strict security or long approval processes such as government projects.
- Using Power FX, custom pages, Power Automate cloud flows, Sharepoint, JavaScript web resources, and Word template files with VBA macros, a dynamic templating engine can be created to serve complex documentation needs.
- This approach allows for the creation of document templates that are not only highly flexible due to the capabilities of VBA macros but are also directly connected to live data exported from Power Platform components.
- The solution detailed by Alex Shlega [MVP] enhances the Power Platform's capabilities by facilitating the passing of parameters to custom pages and solves the challenge of identifying the driveid and fileid for files newly stored in Sharepoint.
- Demonstrations and source files for the described templating engine are made accessible to provide a practical insight into its implementation and potential application in similar scenarios.
Exploring the World of Complex Document Templating
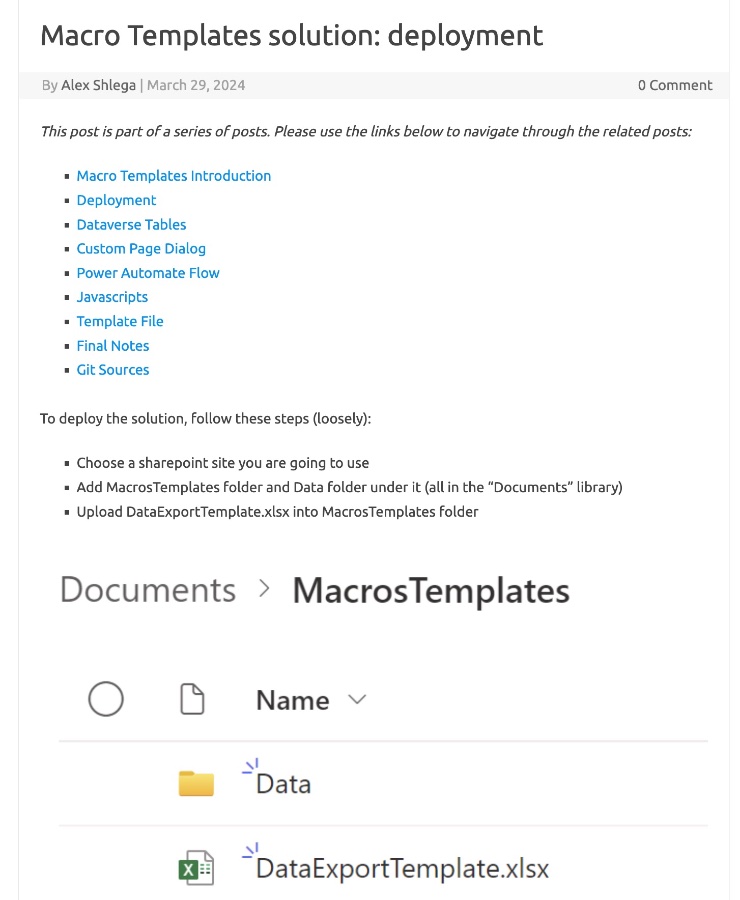
Dataverse Tables Macro Templates solution deployment can be challenging due to strict security, missing subscriptions, and lengthy approvals, especially in government projects. However, this leads to unique tool and technology combinations. In this series, we'll explore one such case.
The need for document templates in a project led to the discovery that traditional templates in Microsoft Dataverse were insufficient. Alternatives like Word templates in Power Automate were considered but found to be difficult for end users to manage and support.
The breakthrough came when the team learned about templates created with VBA Macros in Word, which were highly flexible and data-connected. This realization led to the creation of a templating engine using Power FX, custom page-based dialogues, Power Automate, SharePoint, and JavaScript web resources.
This engine supports complex Word template files with VBA macros, maintaining a live connection to data exported just moments before. This solution showcases the versatility of the Power Platform, including the handling of custom pages and Sharepoint integration.
- Exploring unique combinations of tools and technologies in project solutions
- Overcoming the limitations of traditional document templates with VBA Macros in Word
- Creating a templating engine that integrates Power FX, Power Automate, SharePoint, and more
Read the full article Dataverse Tables Macro Templates solution: deployment

People also ask
What is the difference between standard data model and enhanced data model?
The distinction between the Standard and Enhanced Data Models lies in their structural configuration for managing website data. The Standard Data Model primarily leverages custom tables to organize website settings, whereas the Enhanced Data Model adopts a more complex approach by utilizing a mix of system tables, non-configuration tables, and virtual tables. This blend allows the Enhanced Data Model to minimize the dependence on custom configurations for achieving similar outcomes.
What is enhanced data model?
The Enhanced Data Model is a sophisticated architecture comprising system tables, non-configuration tables, and virtual tables. It is designed to simplify the data management process within the Dataverse ecosystem. By integrating system tables that come pre-packaged with every Dataverse organization, the necessity for additional installations is mitigated, streamlining operational efficiency.
What is metadata in Powerapps?
Metadata, essentially data about data, plays a crucial role in the Dataverse by offering a flexible platform for defining the data structure within an environment. It incorporates a compilation of tables, with each table detailing the type of data stored. This framework facilitates ease of modification in data definitions, aligning with specific application requirements.
What is schema name in Dataverse?
In Dataverse, the SchemaName represents the identifier used for generating database tables. This identifier supports mixed-case usage, allowing developers to define the case sensitivity of object names utilized for strongly-typed programming or REST endpoint interactions. The flexibility in case usage enables precise naming conventions tailored to development needs.
Keywords
Dataverse Tables Macro Templates Deployment, Dataverse Deployment Solution, Macro Templates Deployment, Dataverse Template Solution, Dataverse Macro Deployment, Dataverse Tables Solution, Dataverse Deployment Strategies, Macro Template Solutions Deployment