- All of Microsoft
2023 DAX Updates: Key Changes & Impacts
Explore Transformative DAX Updates in 2023 & Anticipate 2024 Trends with SQLBI
Key insights
DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions, is a formula language used in Microsoft Power BI, Analysis Services, and Power Pivot for Excel. It enables complex calculations and analyses on data from diverse sources. DAX formulas are akin to Excel formulas, but with distinct differences.
In Power BI, DAX is pivotal for creating measures, filtering, sorting data, and making calculated columns. It features context sensitivity, time intelligence, and relational modeling—it adapts to current data contexts, handles date/time functions, and manages table relationships.
- Context sensitivity: DAX refers to current row, column, or page values.
- Time intelligence: DAX has functions for date/time calculations and time-series charts.
- Relational modeling: It crafts and controls table relationships for intricate calculations.
In Excel, DAX empowers Power Pivot for data model creation. It profiles an array of data integrations, robust data modeling capabilities, and comprehensive data analysis through Power Pivot's relationships and calculations.
- Data integration: Power Pivot connects with many data sources.
- Data modeling: Enables relational data model creations for complex analyses.
- Data analysis: Facilitates robust data scrutiny and report generation.
DAX is invaluable for data analysis and visualization across multiple platforms such as Power BI, Analysis Services, or Power Pivot for Excel—essential for data-savvy professionals.
While DAX is consistent across Power BI and Excel in purpose and features such as data integration, data modeling, and data analysis, it differs in context sensitivity and time intelligence capabilities, with Power BI offering broader applications.
Understanding DAX in 2023
The importance of Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) ascended new heights in 2023, becoming a cornerstone for professionals using Microsoft's analytical suite, including Power BI and Excel. The language's continued evolution reflects the growing need for deeper insights into complex datasets, offering tools for high-level analysis and the flexibility to maneuver through different scopes of data—from context-specific calculations to global data modeling. Coming into 2024, we anticipate further enhancements to DAX that will expand its capabilities, potentially offering even greater ease of use and more sophisticated functions to handle the increasingly voluminous and varied data sources that decision-makers need to sift through in the digital age.
What happened in DAX in 2023 A recap of the news in the DAX world in 2023 and a preview of whatSQLBIexpect in 2024.
DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions, is a formula language used in various Microsoft business intelligence tools. It enables complex data calculations and deep data analysis from multiple sources. Unlike Excel formulas, DAX has several key distinctions that offer advanced capabilities.
In Power BI, DAX facilitates the creation of calculated measures, essential for reports and visualizations. It's also instrumental in data filtering, sorting, and the creation of calculated columns. Here's a breakdown of DAX's impact in Power BI:
- Context sensitivity: DAX can act upon data in the current scope, such as rows or pages.
- Time intelligence: DAX possesses functions to handle time and date for period calculations and time-based data visualizations.
- Relational modeling: Establishing and managing inter-table relationships is made possible with DAX, enabling advanced data analysis.
Turning to Excel, DAX's role is linked to Power Pivot data models, allowing connections with various data sources. DAX proves essential in calculating measures and managing data relationships.
- Data integration: Power Pivot connects with many data types, from Excel sheets to SQL databases.
- Data modeling: Power Pivot's relational data model lays the groundwork for sophisticated analysis.
- Data analysis: Power Pivot leverages DAX to delve into data, creating insightful reports and visualizations.
In essence, DAX stands as a robust language, indispensable for anyone engaging with Power BI, Analysis Services, or Excel's Power Pivot. It equips professionals to elevate data visualization and analysis across diverse data landscapes.
To better understand the distinctions between applying DAX in Power BI and Excel, here's a comparison:
| Feature | Power BI | Excel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Create measures, filter/sort data, create columns | Power Pivot models, data connection, data analysis and reporting |
| Context sensitivity | Yes | No |
| Time intelligence | Yes | Limited |
| Relational modeling | Yes | Yes |
| Data integration | Yes | Yes |
| Data modeling | Yes | Yes |
| Data analysis | Yes | Yes |
I hope this helps!
Understanding DAX Further
Dynamics 365 and related business intelligence systems often rely on DAX to turn raw data into actionable insights. With the progression of data analytics, DAX continues to evolve, providing users with an ever-more powerful toolkit for navigating complex datasets. Whether it’s forecasting trends, running What-If scenarios, or revealing hidden patterns, DAX plays a pivotal role in transforming data into a strategic asset for businesses.
A Summary of DAX Developments in 2023
What happened in DAX in 2023? A recap of the news in the DAX world in 2023 and a preview of what we expect in 2024.
DAX, which stands for Data Analysis Expressions, is crucial in Microsoft's business analytics tools. It allows users to perform advanced calculations and analyze data from varied sources. Despite similarities to Excel formulas, DAX offers distinct capabilities.
DAX in Power BI
In Power BI, DAX plays a significant role in manipulating and displaying data. It's used to construct measures for reports and visualizations and also for managing data through filters and sort functionality.
- Context sensitivity: Enables reference to current data points such as rows and columns.
- Time intelligence: Provides functions that work with data and time, perfect for creating complex period calculations and time-series analyses.
- Relational modeling: Facilitates relationship management between tables, essential for comprehensive calculations and analysis.
DAX in Excel
Excel utilizes DAX for Power Pivot data models, a feature that enhances data connectivity and manipulation. It's instrumental in creating data relationships and detailed analyses through data modeling.
- Data integration: Power Pivot extends support for a wide range of data sources.
- Data modeling: Enables sophisticated data model creation for in-depth calculations and analysis.
- Data analysis: Provides tools to evaluate data and compile impactful reports and visualizations.
In essence, DAX is a robust and flexible language vital for analyzing and representing data from multiple sources. It's an indispensable component of Power BI, Analysis Services, or Power Pivot in Excel.
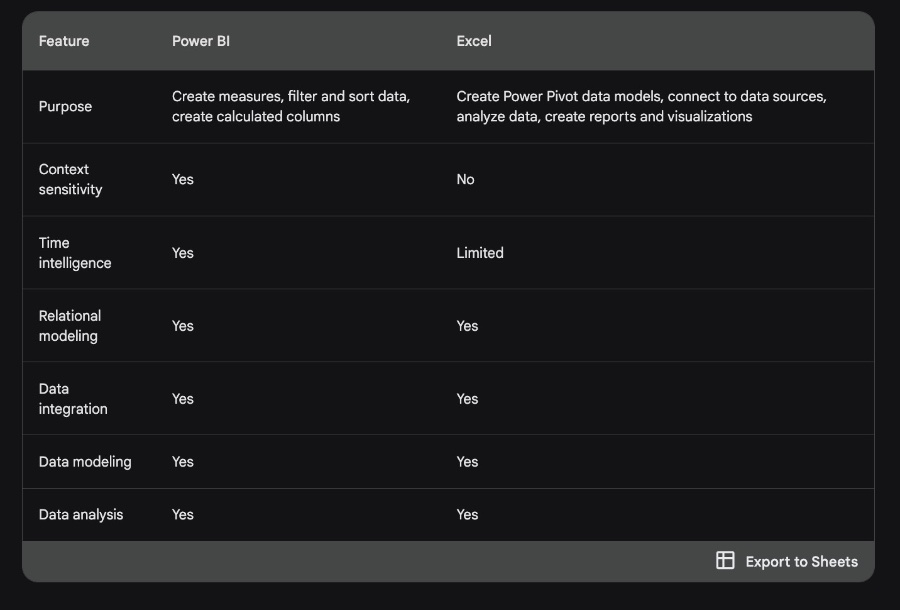
Here's a comparison of the main features of DAX across Power BI and Excel:
Purpose - In Power BI, it is mainly for creating measures, filtering and sorting data, and creating calculated columns. In Excel, it's for building Power Pivot data models, connecting to data sources, and analytics.
Context Sensitivity - Available in Power BI but absent in Excel.
Time Intelligence - Fully supported in Power BI, while only limited in Excel.
Relational Modelling/Data Integration/Data Modelling/Data Analysis - Available in both Power BI and Excel.
I hope this clarifies the role and functionalities of DAX in modern data analysis.

Read the full article What happened in DAX in 2023
## Questions and Answers about Microsoft 365
Keywords
DAX 2023 developments, DAX stock market 2023, German DAX index analysis 2023, DAX performance review 2023, DAX market trends 2023, DAX financial overview 2023, DAX investing insights 2023, DAX economic impact 2023, DAX trading outcomes 2023, DAX yearly summary 2023
