
Mastering Power Apps: Essential YAML Integration Guide
Explore YAML & Power Apps: Master the Basics, Utilize Enhanced Features & Uncover What Lies Ahead in App Development!
Key insights
- YAML is not a full programming language but a human-readable markup alternative to XML and JSON.
- Writing and syntax in YAML involves white spaces for nesting rather than the use of brackets or tags.
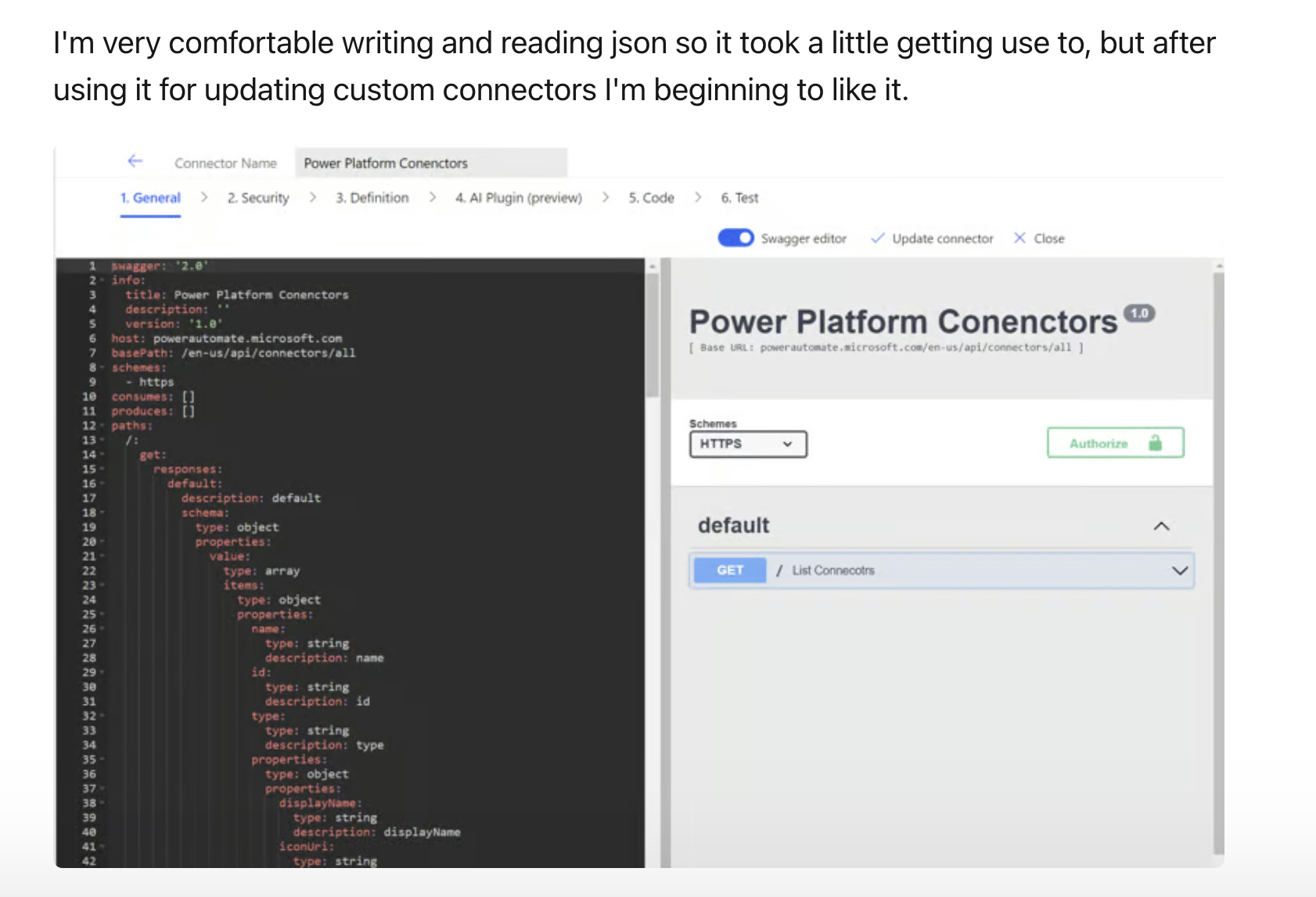
- Power Apps components use JSON internally but YAML can be used externally to manage component properties.
- Editing YAML in Power Apps is currently done by copying code outside, editing, then pasting it back, limited by not being directly editable in the app.
- The future enhancements in YAML integration within Power Apps are anticipated to significantly streamline and enhance developer efficiency, though currently, it's in preview with limited capabilities.
Overview of YAML in Power Apps
YAML, standing for Yet Another Markup Language, offers a simplified code-writing experience primarily aimed at enhancing human readability and ease of configuration management across various platforms including Power Apps. This characteristic makes YAML a preferred format for configuration files and data exchange. Unlike JSON or XML, which utilize brackets and tags, YAML relies on indentation to distinguish code hierarchy, which can simplify the task but also requires precise space management to avoid errors in large or complex scripts. Within the context of Power Apps, YAML is harnessed to modify and manage application components. However, as the feature remains in preview, direct editing is not yet possible within Power Apps’ own environment, necessitating a somewhat cumbersome process of copying and pasting code into external editors for modifications. Looking forward, the integration of more robust YAML editing tools directly within Power Apps promises to unleash much greater efficiency and ease for developers, potentially changing the way coding is approached in the platform.
Read the full article Power Apps and Yaml

Power Apps and YAML have been exciting topics since their announcement at Build. The inability to fully utilize them has led to a deeper exploration into their functionalities and potential benefits.
- What is YAML
- YAML Basics
- Power Apps YAML
- How to Use it
- The Future
YAML stands for Yet Another Markup Language, which lacks computational logic but excels in being human-readable. This simplicity is reminiscent of Python, offering an alternative to XML and JSON.
Adjusting from JSON to YAML can be challenging due to its reliance on indentation to express hierarchy rather than the use of explicit marks used in other markup languages like JSON or XML. However, the learning curve is reasonable, and it integrates smoothly with Power Apps's custom connectors.
In YAML, unlike JSON, data types are dynamically determined, which means there is no need to predefine types, giving it flexibility. Moreover, YAML handles multi-line strings using specific characters to improve readability and maintain textual formatting.
Regarding Power Apps, YAML uses a simpler syntax for data attribution that begins with an '=', making it easier to manipulate without unexpected errors. This integration allows for modifications through a platform like Visual Studio Code, although direct editing in Power Apps is not yet implemented.
Currently, YAML functionality within Power Apps is limited to viewing and copying component code, making bulk editing cumbersome. Despite this, its potential for streamlining and optimizing app development is significant once full integration is achieved.
Exploring YAML in Power Apps
YAML's role in Power Apps revolves around enhancing the user experience in app development. With its straightforward markup style and easy-to-learn syntax, YAML is positioned to be a vital tool in the development process. The anticipated updates to Power Apps that would allow direct YAML editing are expected to simplify component adjustments, providing a much faster and more efficient development workflow. Professionals looking forward to these features are optimistic about the future integration and the advancements it would bring to custom app development.
People also ask
"What are 3 types of Power Apps?"
Answer: Power Apps come in three primary variants: Canvas apps, allowing for a highly tailored user interface with a drag-and-drop experience; model-driven apps, which automatically generate the UI based on the underlying data model; and portal apps, designed to provide external users with secure access to specific data.
"What are Power Apps used for?"
Answer: Power Apps are primarily utilized to build custom business applications without requiring extensive programming knowledge. These apps streamline, automate, and transform business processes and tasks across a variety of industries, enhancing overall efficiency and productivity.
"What is the difference between Power Apps and Power Automate?"
Answer: The main distinction between Power Apps and Power Automate lies in their core functionalities: Power Apps is used to develop custom applications suited to business needs, whereas Power Automate focuses on automating workflows and tasks across various applications and services to enhance efficiency and minimize manual inputs.
"What is better than Power Apps?"
Answer: While "better" is subjective and depends on specific business needs, alternatives like Google AppSheet offer similar functionalities for building custom applications. The choice largely hinges on the user's requirement for integration, ease-of-use, and scalability within the broader ecosystem of tools they employ.
Keywords
Power Apps YAML tutorial, YAML in Power Apps, Power Apps YAML integration, using YAML with Power Apps, Power Apps YAML configuration, Power Apps YAML guide, automate PowerApps with YAML, YAML scripts for Power Apps